 |
|
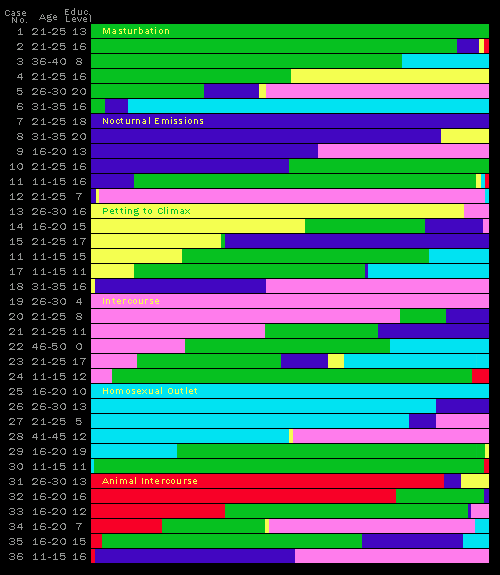
Figure 31. Diverse examples of combinations of six sources of outlet. Each bar shows a combination of outlets used by one individual |
|
“Educ. level 0-8 years” grade school “Educ. level 9-12 years” high school “Educ. level 13-16 years” college “Educ. level 17-20 years” postgraduate |
 |